Home
Menu
Private Dining
Chefs
Contact
Storage
New Page
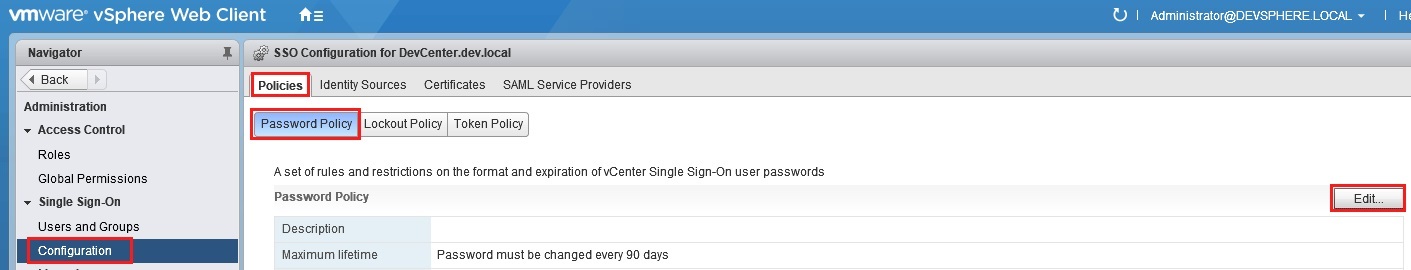
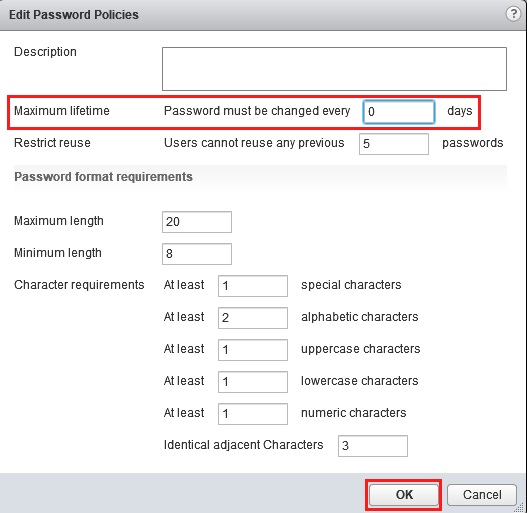
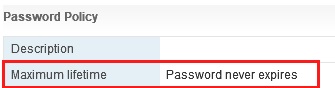
HP MSA 1040 2040 Storage
استوریج HP MSA 1040 2040 نسل جدید استوریج های Small-Midsize شرکت HP می باشد که در آنها قابلیت Tiering اضافه شده است.
برای راه اندازی و مدیزیت این استوریج ها باید کاربر آن دانش لازم در حوزه های زیر را داشته باشد:
- دانش کافی شبکه
- پیکربندی دستگاه استوریج
- مدیریت شبکه SAN
- داشتن معلومات کافی در مورد شبکه های DAS و NAS
- آشنایی کامل با پروتکل های ارتباطی شبکه SAN
کتاب های الکترنیکی مرتبط
• HP MSA System Racking Instructions
• HP MSA 1040 Installation Guide
• HP MSA 1040 System Cable Configuration Guide
• HP MSA 1040 User Guide
• HP MSA 1040 SMU Reference Guide
• HP MSA 1040 CLI Reference Guide
• HP MSA 2040 Installation Guide
• HP MSA 2040 System Cable Configuration Guide
• HP MSA 2040 User Guide
• HP MSA 2040 SMU Reference Guide
• HP MSA 2040 CLI Reference Guide
در صورت نیاز می توانید به آدرس های زیر مراجعه فرمایید.
HP MSA 1040 hp.com/go/msa1040
HP MSA 2040 hp.com/go/msa2040
معرفی
استوریج HP MSA 1040 برای محیط های کوچک که نیاز به پروتکل های 8Gb Fibre Channel و 6/12Gb SAS و 1GbE و 10GbE دارند مناسب می باشد.
استوریج MSA 1040 نسل چهارم از معماری این استوریج می باشد که با یک پردازنده جدید ارائه می شود و دارای دو پورت هاست در هر کنترلر و میزان 4 گیگابایت حافظه Cache در هر کنترلر می باشد.
ویژگی های کلی این استوریج را در ذیل می توانید ببینید:
• کنترلر جدید با معماری و پردازنده جدید
• حافظه کش 4 گیگابایتی در هر کنترلر
• ارتباط SAS با سرعت 6 و 12 گیگابیت بر ثانیه
• قابلیت افزایش فضای ذخیره سازی از طریق کابلهای SAS
• دو پورت هاست در هر کنترلر
• ارتباط 4 و 8 گیگابیت بر ثانیه فیبر
• ارتباط iSCSI با سرعت 1 و 10 گیگابیت اترنت
• قابلیت Expand تا 4 محفظه Enclosure دیگر
• پشتیبانی از 99 دیسک SFF
• پشتیبانی از Thin-Provisioning که نیازمند خرید لایسنس می باشد.
• سیستم مدیریت وب جدید
• پشتیبانی از Sub-LUN Tiering که نیازمند خرید لایسنس می باشد.
• قابلیت Wide Striping که نیازمند خرید لایسنس می باشد و در آن شما می توانید تعداد هارد دیسک زیادی به یک Volume اختصاص بدهید تا بتوانید Performance را بالا ببریم.
استوریج HP MSA 2040 یک استوریج با کارایی بسیار بالا می باشد که دارای سرعت 8 الی 16 گیگابیت بر ثانیه فیبر برای انتقال داده و ارتباط 6 و 12 گیگابیت بر ثانیه SAS و ارتباط iSCSI با سرعت های 1 و 10 گیگابیت اترنت و چهار پورت هاست در هر کنترلر می باشد. استوریج MSA 2040 برای مشتریانی که بدنبال Performance بالا و قیمت پایین می باشند گزینه مناسبی می باشد و همچنین با توجه به قابلیت های موجود این دستگاه برای راهکارهای جامع و مجازی سازی نیز یکی از گزینه های اصلی می باشد.
ویژگی های کلی این استوریج را در ذیل می توانید ببینید:
• کنترلر جدید با معماری و پردازنده جدید
• حافظه کش 4 گیگابایتی در هر کنترلر
• پشتیبانی از هارد های SSD
• 4 host ports per controller
• ارتباط 4 و 8 و 16 گیگابیت بر ثانیه فیبر
• ارتباط SAS با سرعت 6 و 12 گیگابیت بر ثانیه
• ارتباط iSCSI با سرعت 1 و 10 گیگابیت اترنت
• پشتیبانی همزمان از FC و iSCSI در یک کنترلر
• قابلیت Expand تا 8 محفظه Enclosure دیگر
• پشتیبانی از 199 دیسک SFF
• قابلیت پشتیبانی از FDE Full Drive Encryption بوسیله SED
• پشتیبانی از Thin-Provisioning
• پشتیبانی از Sub-LUN Tiering
• پشتیبانی از Read Cache
• قابلیت پشتیبانی از Performance Tier با خرید لایسنس
• سیستم مدیریت وب جدید
• قابلیت Wide Striping که نیازمند خرید لایسنس می باشد و در آن شما می توانید تعداد هارد دیسک زیادی به یک Volume اختصاص بدهید تا بتوانید Performance را بالا ببریم. برای مثال 16 دیسک برای یک Volume
• GL200 Firmware
• تنها هارد های SSD و SED در این استوریج ساپورت می شوند.
استوریج HP MSA 2040 با توجه به هاردهای SSD کارایی بالایی را ارائه می کند. با توجه به قابلیت Performance Tier و وجود هارد های SSD بالاترین performance ممکن را در محیط های اشتراکی و مجازی ارائه می نماید.
استوریج های HP MSA 1040/2040 با یک لایسنس 64 Snapshots و Volume Copy برای بالا بردن درصد Data Protection می آیند. لایسنس دیگری به نام Snapshots 512 وجود دارد که خرید آن بصورت Optional می باشد. این دستگاه می تواند با دستگاههایی نظیر P2000 G3 و MSA 1040 و MSA 2040 و با استفاده از پروتکل های FC و iSCSI عملیات Replication را انجام دهد. این عملیات با استفاده از ویژگی Remote Snap دستگاه صورت می پذیرد.
اصطلاحات
VirtualDisk Vdisk: واژه Vdisk با نام Disk Group تعویض شده است. در استوریج های خطی Linear و نیز SMU ورژن 2 از واژه Vdisk استفاده شده است. برای استوریج های مجازی و ورژن سوم SMU از واژه Disk Group استفاده شده است. در واقع Vdisk و Disk Group اساسا یک تعریف را دارند.
Vdisk ها دارای انواع RAID بیشتری مانند NRAID ، RAID0 ، RAID3 می باشند که قابل راه اندازی در محیط CLI و نیز RAID50 با قابلیت راه اندازی در هر دو محیط CLI و SMU می باشند.
Linear Storage: Linear Storage is the traditional storage that has been used for the four MSA generations. With Linear Storage, the user specifies which drives make up a RAID Group and all storage is fully allocated.
Virtual Storage: Virtual Storage is an extension of Linear Storage. Data is virtualized not only across a single disk group, as in the linear implementation, but also across multiple disk groups with different performance capabilities and use cases.
Disk Group: A Disk Group is a collection of disks in a given redundancy mode (RAID 1, 5, 6, or 10 for Virtual Disk Groups and NRAID and RAID 0, 1, 3, 5, 6, 10, or 50 for Linear Disk Groups). A Disk Group is equivalent to a Vdisk in Linear Storage and utilizes the same proven fault tolerant technology used by Linear Storage. Disk Group RAID level and size can be created based on performance and/or capacity requirements. With GL200 or newer firmware multiple Virtual Disk Groups can be allocated into a Storage Pool for use with the Virtual Storage features; while Linear Disk Groups are also in Storage Pools, there is a one-to-one correlation between Linear Disk Groups and their associated Storage Pools.
Storage Pools: The GL200 firmware or newer introduces Storage Pools which are comprised of one or more Virtual Disk Groups or one Linear Disk Group. For Virtual Storage, LUNs are no longer restricted to a single disk group as with Linear Storage. A volume’s data on a given LUN can now span all disk drives in a pool. When capacity is added to a system, users will benefit from the performance of all spindles in that pool.
When leveraging Storage Pools, the MSA 1040/2040 supports large, flexible volumes with sizes up to 128TB and facilitates seamless capacity expansion. As volumes are expanded data automatically reflows to balance capacity utilization on all drives.
LUN (Logical Unit Number): The MSA 1040/2040 arrays support 512 volumes and up to 512 snapshots in a system. All of these volumes can be mapped to LUNs. Maximum LUN sizes are up to 128TB and the LUNs sizes are dependent on the storage architecture: Linear vs. Virtualized. Thin Provisioning allows the user to create the LUNs independent of the physical storage.
Thin Provisioning: Thin Provisioning allows storage allocation of physical storage resources only when they are consumed by an application. Thin Provisioning also allows over-provisioning of physical storage pool resources allowing ease of growth for volumes without predicting storage capacity upfront.
Thick Provisioning: All storage is fully allocated with Thick Provisioning. Linear Storage always uses Thick Provisioning.
Tiers: Disk tiers are comprised of aggregating 1 or more Disk Groups of similar physical disks. The MSA 2040 supports 3 distinct tiers:
1. A Performance tier with SSDs
2. A Standard SAS tier with Enterprise SAS HDDs
3. An Archive tier utilizing Midline SAS HDDs
Prior to GL200 firmware, the MSA 2040 operated through manual tiering, where LUN level tiers are manually created and managed by using dedicated Vdisks and volumes. LUN level tiering requires careful planning such that applications requiring the highest performance be placed on Vdisks utilizing high performance SSDs. Applications with lower performance requirements can be placed on Vdisks comprised of Enterprise SAS or Midline SAS HDDs. Beginning with GL200 or newer firmware, the MSA 2040 now supports Sub-LUN Tiering and automated data movement between tiers.
The MSA 2040 automated tiering engine moves data between available tiers based on the access characteristics of that data. Frequently accessed data contained in “pages” will migrate to the highest available tier delivering maximum I/O’s to the application. Similarly, “cold” or infrequently accessed data is moved to lower performance tiers. Data is migrated between tiers automatically such that I/O’s are optimized in real-time.
The Archive and Standard Tiers are provided at no charge on the MSA 2040 platform beginning with GL200 or newer firmware. The Performance Tier utilizing a fault tolerant SSD Disk Group is a paid feature that requires a license. Without the Performance Tier license installed, SSDs can still be used as Read Cache with the Sub-LUN Tiering feature. Sub-LUN Tiering from SAS MDL (Archive Tier) to Enterprise SAS (Standard Tier) drives is provided at no charge.
Note
The MSA 1040 only supports the Standard and Archive Tiers, and requires a license to enable Sub-LUN Tiering and other Virtual Storage features such as Thin Provisioning.
Read Cache: Read Cache is an extension of the controller cache. Read Cache allows a lower cost way to get performance improvements from SSD drives.
Sub-LUN Tiering: Sub-LUN Tiering is a technology that allows for the automatic movement of data between storage tiers based on access trends. In the MSA 1040/2040, Sub-LUN Tiering places data in a LUN that is accessed frequently in higher performing media while data that is infrequently accessed is placed in slower media.
Page: An individual block of data residing on a physical disk. For Virtual Storage, the page size is 4 MB.
General best practices
Use version 3 of the Storage Management Utility
With the release of the GL200 firmware, there is an updated version of the Storage Management Utility (SMU). This new Web Graphical User Interface (GUI) allows the user to use the new features of the GL200 firmware. This is version 3 of the SMU (V3).
SMU V3 is the recommended Web GUI. SMU V3 can be accessed by adding “/v3” to the IP address of the MSA array: https://<MSA array IP>/v3
The recommended Web GUI is SMU V2 if you are using the replication features of the MSA 1040/2040. SMU V2 can be accessed by adding “/v2” to the IP address of the MSA array: https://<MSA array IP>/v2
Become familiar with the array by reading the manuals
The first recommended best practice is to read the corresponding guides for either the HP MSA 1040 or HP MSA 2040. These documents include the User Guide, the Storage Management Utility (SMU) Reference Guide, or the Command Line Interface (CLI) Reference Guide. The appropriate guide will depend on the interface that you will use to configure the storage array. Always operate the array in accordance with the user manual. In particular, never exceed the environmental operation requirements.
Other HP MSA 1040 and HP MSA 2040 materials of importance to review are:
• The HP MSA Remote Snap Technical white paper located at: h20195.www2.hp.com/v2/GetPDF.aspx/4AA1-0977ENW.pdf
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
The recommended practice would be to use initiator nicknaming as outlined in figure 1, host aggregating of initiators and the grouping of hosts using V3 SMU.
Disk Group initialization for Linear Storage
During the creation of a Disk Group for Linear Storage, the user has the option to create a Disk Group in online mode (default) or offline mode. If the “online initialization” option is enabled, you can use the Disk Group while it is initializing. Online initialization takes more time because parity initialization is used during the process to initialize the Disk Group. Online initialization is supported for all HP MSA 1040/2040 RAID levels except for RAID 0 and NRAID. Online initialization does not impact fault tolerance.
If the “online initialization” option is unchecked, which equates to “offline initialization,” you must wait for initialization to complete before using the Disk Group for Linear Storage, but the initialization takes less time to complete.
Figure 2. Choosing online or offline initialization
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Best practice for monitoring array health
Setting up the array to send notifications is important for troubleshooting and log retention.
Configure email and SNMP notifications
The Storage Management Utility (SMU) version 3 is the recommended method for setting up email and SNMP notifications. Setting up these services is easily accomplished by using a Web browser; to connect; type in the IP address of the management port of the HP MSA 1040/2040.
Email notifications can be sent to up to as many as three different email addresses. In addition to the normal email notification, enabling managed logs with the “Include logs as an email attachment” option enabled is recommended. When the “Include logs as an email attachment” feature is enabled, the system automatically attaches the system log files to the managed logs email notifications sent. The managed logs email notification is sent to an email address which will retain the logs for future diagnostic investigation.
The MSA 1040/2040 storage system has a limited amount of space to retain logs. When this log space is exhausted, the oldest entries in the log are overwritten. For most systems this space is adequate to allow for diagnosing issues seen on the system. The managed logs feature notifies the administrator that the logs are nearing a full state and that older information will soon start to get overwritten. The administrator can then choose to manually save off the logs. If “Include logs as an email attachment” is also checked, the segment of logs which is nearing a full state will be attached to the email notification. Managed logs attachments can be multiple MB in size.
Enabling the managed logs feature allows log files to be transferred from the storage system to a log-collection system to avoid losing diagnostic data. The “Include logs as an email attachment” option is disabled by default.
HP recommends enabling SNMP traps. Version 1 SNMP traps can be sent to up to three host trap addresses (i.e., HP SIM Server or other SNMP server). To send version 3 SNMP traps, create a SNMPv3 user with the Trap Target account type. Use SNMPv3 traps rather than SNMPv1 traps for greater security. SNMP traps can be useful in troubleshooting issues with the MSA 1040/2040 array.
To configure email and version 1 SNMP settings in the SMU, click Home -> Action -> Set Up Notifications.
Enter the correct information for email, SNMP, and Managed Logs. See figure 4.
Figure 3. Setting Up Management services
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Figure 4. SNMP, Email, and Managed Logs Notification Settings
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
To configure SNMPv3 users and trap targets, click Home | Action | Manage Users. See figure 5.
Figure 5. Manage Users
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Enter the correct information for SNMPv3 trap targets. See figure 6.
Figure 6. User Management
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Setting the notification level for email and SNMP
Setting the notification level to Warning, Error, or Critical on the email and SNMP configurations will ensure that events of that level or above are sent to the destinations (i.e., SNMP server, SMTP server) set for that notification. HP recommends setting the notification level to Warning.
HP MSA 1040/2040 notification levels:
• Warning will send notifications for all Warning, Error, or Critical events.
• Error will only send Error and Critical events.
• Critical will only send Critical events.
Sign up for proactive notifications for the HP MSA 1040/2040 array
Sign up for proactive notifications to receive MSA product advisories. Applying the suggested resolutions can enhance the availability of the product.
Sign up for the notifications at: hp.com/go/myadvisory
Best practices for provisioning storage on the HP MSA 1040/2040
The release of the GL200 firmware for the MSA 1040/2040 introduces virtual storage features such as Thin Provisioning and Sub-LUN Tiering. The section below will assist in the best methods for optimizing these features for the MSA 1040/2040.
Thin Provisioning
Thin Provisioning is a storage allocation scheme that automatically allocates storage as your applications need it.
Thin provisioning dramatically increases storage utilization by removing the equation between allocated and purchased capacity. Traditionally, application administrators purchased storage based on the capacity required at the moment and for future growth. This resulted in over-purchasing capacity and unused space.
With Thin Provisioning, applications can be provided with all of the capacity to which they are expected to grow but can begin operating on a smaller amount of physical storage. As the applications fill their storage, new storage can be purchased as needed and added to the array’s storage pools. This results in a more efficient utilization of storage and a reduction in power and cooling requirements.
Thin provisioning is enabled by default for virtual storage. The overcommit setting only applies to virtual storage and simply lets the user oversubscribe the physical storage (i.e., provision volumes in excess of physical capacity). If a user disables overcommit, they can only provision virtual volumes up to the available physical capacity. Snapshots are allowed for virtual volumes only with overcommit enabled. The overcommit setting is not applicable on traditional linear storage.
Overcommit is performed on a per pool basis and using the “Change Pool Settings” option. To change the Pool Settings to overcommit disabled:
1. Open V3 of the SMU and select “Pools”
2. Click “Change Pool Settings”
3. Uncheck the “Enable overcommitment of pool?” by clicking the box.
Figure 7. Changing Pool Settings
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Figure 8. Disabling the overcommit of the pool
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Thresholds and Notifications
If you use Thin Provisioning, monitor space consumption and set notification thresholds appropriately for the rate of storage consumption. The thresholds and notifications below can help determine when more storage needs to be added.
Users with a manage role can view and change settings that affect the thresholds and corresponding notifications for each storage pool.
• Low Threshold—When this percentage of pool capacity has been used, Informational event 462 is generated to notify the administrator. This value must be less than the Mid Threshold value. The default is 25%.
• Mid Threshold—When this percentage of pool capacity has been used, Warning event 462 is generated to notify the administrator to add capacity to the pool. This value must be between the Low Threshold and High Threshold values. The default is 50%. If the over-commitment setting is enabled, the event has Informational severity; if the over-commitment setting is disabled, the event has Warning severity.
• High Threshold—When this percentage of pool capacity has been used, Warning event 462 is generated to alert the administrator that it is critical to add capacity to the pool. This value is automatically calculated based on the available capacity of the pool minus reserved space. This value cannot be changed by the user.
T10 Unmap for Thin Reclaim
Unmap is the ability to reclaim thinly provisioned storage after the storage is no longer needed.
There are procedures to reclaim unmap space when using Thin Provisioning and ESX.
The user should run the unmap command with ESX 5.0 Update 1 or higher to avoid performance issues.
In ESX 5.0, unmap is automatically executed when deleting or moving a Virtual Machine.
In ESX 5.0 Update 1 and greater, the unmap command was decoupled from auto reclaim; therefore, use the VMware® vSphere CLI command to run unmap command.
See VMware documentation for further details on the unmap command and reclaiming space.
Pool Balancing
Creating and balancing storage pools properly can help with performance of the MSA array. HP recommends keeping pools balanced from a capacity utilization and performance perspective. Pool balancing will leverage both controllers and balance the workload across the two pools.
Assuming symmetrical composition of storage pools, create and provision storage volumes by the workload that will be used. For example, an archive volume would be best placed in a pool with the most available Archive Tier space. For a high performance volume, create the Disk Group on the pool that is getting the least amount of I/O on the Standard and Performance Tiers.
Determining the pool space can easily be viewed in V3 of the SMU. Simply navigate to “Pools” and click the name of the pool.
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Viewing the performance of the pools or Virtual Disk Groups can also assist in determining where to place the Archive Tier space.
From V3 of the SMU, navigate to “Performance” then click “Virtual Pools” from the “Show:” drop-down box. Next, click the pool and for real time data, click “Show Data”. For Historical Data, click the “Historical Data” box and “Set time range”.
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Tiering
A Tier is defined by the disk type in the Virtual Disk Groups.
• Performance Tier contains SSDs
• Standard Tier contains 10K RPM/15K RPM Enterprise SAS drives
• Archive Tier contains MDL SAS 7.2K RPM drives
Disk Group Considerations
With the GL200 firmware on the MSA, allocated pages are evenly distributed between disk groups in a tier; therefore, create all disk groups in a tier with the same RAID type and number of drives to ensure uniform performance in the tier.
Consider an example where the first Disk Group in the Standard Tier consists of five 15K Enterprise SAS drives in a RAID 5 configuration. To ensure consistent performance in the tier, any additional disk groups for the Standard Tier should also be a RAID 5 configuration. Adding a new disk group configured with four 10K Enterprise SAS drives in a RAID 6 configuration will produce inconsistent performance within the tier due to the different characteristics of the disk groups.
For optimal write performance, parity based disk groups (RAID 5 and RAID 6) should be created with “The Power of 2” method. This method means that the number of data (non-parity) drives contained in a disk group should be a power of 2. See the chart below.
RAID Type
Total Drives per Disk Group
Data Drives
Parity Drives
RAID 5
3
2
1
RAID 5
5
4
1
RAID 5
9
8
1
RAID 6
4
2
2
RAID 6
6
4
2
RAID 6
10
8
2
Due to the limitation of Disk Groups in a pool, which is 16, RAID type should be considered when creating new Disk Groups. For example, instead of creating multiple RAID 1 Disk Groups, consider using a larger RAID 10 Disk Group.
Drive Type and Capacity Considerations when using Tiering
All hard disk drives in a tier should be the same type. For example, do not mix 10K RPM and 15K RPM drives in the same Standard Tier.
If you have a Performance Tier on the MSA 2040, consider sizing the Performance Tier to be 5%–10% the capacity of the Standard Tier.
Disk Group RAID Type Considerations
RAID 6 is recommended when using large capacity Midline (MDL) SAS drives in the Archive Tier. The added redundancy of RAID 6 will protect against data loss in the event of a second disk failure with large MDL SAS drives.
RAID 5 is commonly used for the Standard Tier where the disks are smaller and faster resulting in shorter rebuild times. RAID 5 is used in workloads that typically are both random and sequential in nature.
See the Best practices for SSDs section for RAID types used in the Performance Tier and Read Cache.
Global Spares with Tiers
Using Global spares is recommended for all tiers based on spinning media. When using these global spares, make sure to use the same drive types as the Disk Group. The drive size must be equal or larger than the smallest drive in the tier.
Expanding Virtual Volumes
There might come a time when the Virtual Disk Group in a pool will start to fill up. To easily add more space, the MSA implements Wide Striping to increase the size of the virtual volumes. The recommended method to increase the volume size is to add a new Virtual Disk Group with the same amount of drives and RAID type as the existing Virtual Disk Group has.
For example, a Virtual Disk Group in pool A is filling up. This Disk Group is a five 300GB drive, 15K RPM, RAID 5 Disk Group. The recommended procedure would be to create a new Virtual Disk Group on pool A that also has five, 300GB 15K disk drives in a RAID 5 configuration.
Best practices when choosing drives for HP MSA 1040/2040 storage
The characteristics of applications and workloads are important when selecting drive types for the HP MSA 1040/2040 array.
Drive types
The HP MSA 1040 array supports SAS Enterprise drives and SAS Midline (MDL) drives. The HP MSA 2040 array supports SSDs, SAS Enterprise drives, SAS Midline (MDL) drives, and Self-Encrypting Drives (SED). See the Full Disk Encryption section below for more information on SED drives. The HP MSA 1040/2040 array does not support Serial ATA (SATA) drives. Choosing the correct drive type is important; drive types should be selected based on the workload and performance requirements of the volumes that will be serviced by the storage system. For sequential workloads, SAS Enterprise drives or SAS MDL drives provide a good price-for-performance tradeoff over SSDs. If more capacity is needed in your sequential environment, SAS MDL drives are recommended. SAS Enterprise drives offer higher performance than SAS MDL and should also be considered for random workloads when performance is a premium. For high performance random workloads, SSDs would be appropriate when using the MSA 2040 array.
SAS MDL drives are not recommended for constant high workload applications. SAS MDL drives are intended for archival purposes.
Best practices to improve availability
There are many methods to improve availability when using the HP MSA 1040/2040 array. High availability is always advisable to protect your assets in the event of a device failure. Outlined below are some options that will help you in the event of a failure.
Volume mapping
Using volume mapping correctly can provide high availability from the hosts to the array. For high availability during a controller failover, a volume must be mapped to at least one port accessible by the host on both controllers. Mapping a volume to ports on both controllers ensures that at least one of the paths is available in the event of a controller failover, thus providing a preferred/optimal path to the volume.
In the event of a controller failover, the surviving controller will report that it is now the preferred path for all Disk Groups. When the failed controller is back online, the Disk Groups and preferred paths switch back to the original owning controller.
Best practice is to map volumes to two ports on each controller to take advantage of load balancing and redundancy to each controller.
Mapping a port will make a mapping to each controller; thus, mapping port 1 will map host ports A1 and B1. Mapping to port 2 will map host ports A2 and B2.
With this in mind, make sure that physical connections are set up correctly on the MSA, so that a server has a connection to both controllers on the same port number. For example, on a direct attach MSA 2040 SAS with multiple servers, make sure that ports A1 and B1 are connected to server A, ports A2 and B2 are connected to server B, and so on.
Figure 9. Direct Attach Cabling
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
It is not recommended to enable more than 8 paths to a single host, i.e., 2 HBA ports on a physical server connected to 2 ports on the A controller and 2 ports on the B controller. Enabling more paths from a host to a volume puts additional stress on the operating system’s multipath software which can lead to delayed path recovery in very large configurations.
Note
Volumes should not be mapped to multiple servers at the same time unless the operating systems on the servers are cluster aware. However, since a server may contain multiple unique initiators, mapping a volume to multiple unique initiators (that are contained in the same server) is supported and recommended. Recommended practice is to put multiple initiators for the same host into a host and map the host to the LUNs, rather than individual maps to initiators.
Redundant paths
To increase the availability of the array to the hosts, multiple, redundant paths should be used along with multipath software. Redundant paths can also help in increasing performance from the array to the hosts (discussed later in this paper). Redundant paths can be accomplished in multiple ways. In the case of a SAN attach configuration, best practice would be to have multiple, redundant switches (SANs) with the hosts having at least one connection into each switch (SAN), and the array having one or more connections from each controller into each switch. In the case of a direct attach configuration, best practice is to have at least two connections to the array for each server. In the case of a direct attach configuration with dual controllers, best practice would be to have at least one connection to each controller.
Multipath software
To fully utilize redundant paths, multipath software should be installed on the hosts. Multipath software allows the host operating system to use all available paths to volumes presented to the host; redundant paths allow hosts to survive SAN component failures. Multipath software can increase performance from the hosts to the array. Table 1 lists supported multipath software by operating systems.
Note
More paths are not always better. Enabling more than 8 paths to a single volume is not recommended
Table 1. Multipath and operating systems
Operating system
Multipath name
Vendor ID
Product ID
Windows® 2008/2012
Microsoft® multipath I/O (MPIO)
HP
MSA 2040 SAN
MSA 2040 SAS
MSA 1040 SAN
MSA 1040 SAS
Linux®
Device mapper/multipath
HP
MSA 2040 SAN
MSA 2040 SAS
MSA 1040 SAN
MSA 1040 SAS
VMware
Native multipath (NMP)
HP
MSA 2040 SAN
MSA 2040 SAS
MSA 1040 SAN
MSA 1040 SAS
Installing MPIO on Windows Server® 2008 R2/2012
Microsoft has deprecated servermanagercmd for Windows Server 2008 R2 so you will use the ocsetup command instead.
1. Open a command prompt window and run the following command:
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Note
There are 6 spaces between HP and MSA in the mpclaim command.
The mpclaim –n option avoids rebooting. Reboot is required before MPIO is operational.
The MPIO software is installed. When running the mpclaim command, type in the correct product ID for your MSA product. See table 1 above.
2. If you plan on using MPIO with a large number of LUNs, configure your Windows Server Registry to use a larger PDORemovePeriod setting.
–If you are using a Fibre Channel connection to a Windows server running MPIO, use a value of 90 seconds.
–If you are using an iSCSI connection to a Windows server running MPIO, use a value of 300 seconds.
See “Long Failover Times When Using MPIO with Large Numbers of LUNs” below for details.
Once the MPIO DSM is installed, no further configuration is required; however, after initial installation, you should use Windows Server Device Manager to ensure that the MPIO DSM has installed correctly as described in “Managing MPIO LUNs” below.
Long Failover Times When Using MPIO with Large Numbers of LUNs
Microsoft Windows servers running MPIO use a default Windows Registry PDORemovePeriod setting of 20 seconds. When MPIO is used with a large number of LUNs, this setting can be too brief, causing long failover times that can adversely affect applications.
The Microsoft Technical Bulletin Configuring MPIO Timers, describes the PDORemovePeriod setting:
“This setting controls the amount of time (in seconds) that the multipath pseudo-LUN will continue to remain in system memory, even after losing all paths to the device. When this timer value is exceeded, pending I/O operations will be failed, and the failure is exposed to the application rather than attempting to continue to recover active paths. This timer is specified in seconds. The default is 20 seconds. The max allowed is MAXULONG.”
Workaround: If you are using MPIO with a large number of LUNs, edit your registry settings so that HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\mpio\Parameters\PDORemovePeriod is set to a higher value.
• If you are using a Fibre Channel connection to a Windows server running MPIO, use a value of 90 seconds.
• If you are using an iSCSI connection to a Windows server running MPIO, use a value of 300 seconds.
For more information, refer to Configuring MPIO Timers at: technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee619749%28WS.10%29.aspx
Managing MPIO LUNs
The Windows Server Device Manager enables you to display or change devices, paths, and load balance policies, and enables you to diagnose and troubleshoot the DSM. After initial installation of the MPIO DSM, use Device Manager to verify that it has installed correctly.
If the MPIO DSM was installed correctly, each MSA 1040/2040 storage volume visible to the host will be listed as a multi-path disk drive as shown in the following example.
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
To verify that there are multiple, redundant paths to a volume, right-click the Multi-Path Disk Device and select Properties.
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Click the MPIO tab to view the MPIO property sheet, which enables you to view or change the load balance policy and view the number of paths and their status.
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
The Details tab shows additional parameters.
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Dual power supplies
The HP MSA 1040/2040 chassis and supported expansion enclosures ship with dual power supplies. At a minimum, connect both power supplies in all enclosures. For the highest level of availability, connect the power supplies to separate power sources.
Dual controllers
The HP MSA 2040 can be purchased as a single or dual controller system; the HP MSA 1040 is sold only as a dual controller system. Utilizing a dual controller system is best practice for increased reliability for two reasons. First, dual controller systems will allow hosts to access volumes during a controller failure or during firmware upgrades (given correct volume mapping discussed above). Second, if the expansion enclosures are cabled correctly, a dual controller system can withstand an expansion IO Module (IOM) failure, and in certain situations a total expansion enclosure failure.
Reverse cabling of expansion enclosures
The HP MSA 1040/2040 firmware supports both fault tolerant (reverse cabling) and straight-through SAS cabling of expansion enclosures. Fault tolerant cabling allows any expansion enclosure to fail or be removed without losing access to other expansion enclosures in the chain. For the highest level of fault tolerance, use fault tolerant (reverse) cabling when connecting expansion enclosures.
Figure 10. Reverse cabling example using the HP MSA 1040 system
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
See the MSA Cable Configuration Guide for more details on cabling the HP MSA 1040/2040.
The HP MSA 1040/2040 Cable Configuration Guides can be found on the MSA support pages.
For MSA 1040: hp.com/support/msa1040
For MSA 2040: hp.com/support/msa2040
Create Disk Groups across expansion enclosures
HP recommendation is to stripe Disk Groups across shelf enclosures to enable data integrity in the event of an enclosure failure. A Disk Group created with RAID 1, 10, 3, 5, 50, or 6 can sustain one or more expansion enclosure failures without loss of data depending on RAID type. Disk Group configuration should take into account MSA drive sparing methods such as dedicated, global, and dynamic sparing.
Drive sparing
Drive sparing, sometimes referred to as hot spares, is recommended to help protect data in the event of a disk failure in a fault tolerant Disk Group (RAID 1, 3, 5, 6, 10, or 50) configuration. In the event of a disk failure, the array automatically attempts to reconstruct the data from the failed drive to a compatible spare. A compatible spare is defined as a drive that has sufficient capacity to replace the failed disk and is the same media type (i.e., SAS SSD, Enterprise SAS, Midline SAS, or SED drives). The HP MSA 2040 supports dedicated, global, and dynamic sparing. The HP MSA 1040/2040 will reconstruct a critical or degraded Disk Group.
Important
An offline or quarantined Disk Group is not protected by sparing.
Supported spare types:
• Dedicated spare—reserved for use by a specific Disk Group to replace a failed disk. This method is the most secure way to provide spares for Disk Groups. The array supports up to 4 dedicated spares per Disk Group. Dedicated spares are only applicable to Linear Storage.
• Global spare—reserved for use by any fault-tolerant Disk Group to replace a failed disk. The array supports up to 16 global spares per system. At least one Disk Group must exist before you can add a global spare. Global Spares are applicable to both Virtual and Linear Storage.
• Dynamic spare—all available drives are available for sparing. If the MSA has available drives and a Disk Group becomes degraded any available drive can be used for Disk Group reconstruction. Dynamic spares are only applicable to Linear Storage.
Sparing process
When a disk fails in a redundant Disk Group, the system first looks for a dedicated spare for the Disk Group. If a dedicated spare is not available or the disk is incompatible, the system looks for any compatible global spare. If the system does not find a compatible global spare and the dynamic spares option is enabled, the system uses any available compatible disk for the spare. If no compatible disk is available, reconstruction cannot start.
During reconstruction of data, the effected Disk Group will be in either a degraded or critical status until the parity or mirror data is completely written to the spare, at which time the Disk Group returns to fault tolerant status. For RAID 50 Disk Groups, if more than one sub-Disk Group becomes critical, reconstruction and use of spares occurs in the order sub-Disk Groups are numbered. In the case of dedicated spares and global spares, after the failed drive is replaced, the replacement drive will need to added back as a dedicated or global spare.
Best practice for sparing is to configure at least one spare for every fault tolerant Disk Group in the system.
Drive replacement
In the event of a drive failure, replace the failed drive with a compatible drive as soon as possible. As noted above, if dedicated or global sparing is in use, mark the new drive as a spare (either dedicated or global), so it can be used in the future for any other drive failures.
Working with Failed Drives and Global Spares
When a failed drive rebuilds to a spare, the spare drive now becomes the new drive in the Disk Group. At this point, the original drive slot position that failed is no longer part of the Disk Group. The original drive should be replaced with a new drive.
In order to get the original drive slot position to become part of the Disk Group again, do the following:
1. Replace the failed drive with a new drive.
2. When the new drive is online and marked as “Available”, configure the drive as a global spare drive.
3. Fail the drive in the original global spare location by removing it from the enclosure. The RAID engine will rebuild to the new global spare which will then become an active drive in the RAID set again.
4. Replace the drive you manually removed from the enclosure.
5. If the drive is marked as “Leftover”, clear the disk metadata.
6. Re-configure the drive as the new global spare.
Virtual Storage only uses Global sparing. Warnings alerts are sent out when the last Global spare is used in a system.
Implement Remote Snap replication with Linear Storage
The HP MSA 1040/2040 storage system Remote Snap feature is a form of asynchronous replication that replicates block- level data from a volume on a local system to a volume on the same system or on a second independent system. The second system may be at the same location as the first, or it may be located at a remote site.
Best practice is to implement Remote Snap replication for disaster recovery.
Note
Remote Snap requires a purchasable license in order to implement.
To obtain a Remote Snap license, go to: h18004.www1.hp.com/products/storage/software/p2000rs/index.html
See the HP MSA Remote Snap Technical white paper: h20195.www2.hp.com/v2/GetPDF.aspx/4AA1-0977ENW.pdf
Use VMware Site Recovery Manager with Remote Snap replication
VMware vCenter Site Recovery Manager (SRM) is an extension to VMware vCenter that delivers business-continuity and disaster-recovery solution that helps you plan, test, and execute the recovery of vCenter virtual machines. SRM can discover and manage replicated datastores, and automate migration of inventory from one vCenter to another. Site Recovery Manager integrates with the underlying replication product through a storage replication adapter (SRA).
SRM is currently supported on the MSA 1040/2040 in linear mode only.
For best practices with SRM and MSA Remote Snap replication, see the “Integrate VMware vCenter SRM with HP MSA Storage” technical white paper: h20195.www2.hp.com/V2/GetPDF.aspx/4AA4-3128ENW.pdf
Note
This paper was written for the HP MSA P2000, but is also applicable for the MSA 1040/2040 FC and iSCSI models.
Best practices to enhance performance
This section outlines configuration options for enhancing performance for your array.
Cache settings
One method to tune the storage system is by choosing the correct cache settings for your volumes. Controller cache options can be set for individual volumes to improve a volume’s I/O performance.
Caution
Only disable write-back caching if you fully understand how the host operating system, application, and adapter move data. If used incorrectly, you might hinder system performance.
Using write-back or write-through caching
By default, volume write-back cache is enabled. Because controller cache is backed by super-capacitor technology, if the system loses power, data is not lost. For most applications, write-back caching enabled is the best practice. With the transportable cache feature, write-back caching can be used in either a single or dual controller system. See the MSA 1040/2040 User Guide for more information on the transportable cache feature.
You can change a volume’s write-back cache setting. Write-back is a cache-writing strategy in which the controller receives the data to be written to disks, stores it in the memory buffer, and immediately sends the host operating system a signal that the write operation is complete, without waiting until the data is actually written to the disk. Write-back cache mirrors all of the data from one controller module cache to the other unless cache optimization is set to no-mirror. Write-back cache improves the performance of write operations and the throughput of the controller. This is especially true in the case of random I/O, where write-back caching allows the array to coalesce the I/O to the Disk Groups.
When write-back cache is disabled, write-through becomes the cache-writing strategy. Using write-through cache, the controller writes the data to the disks before signaling the host operating system that the process is complete. Write-through cache has lower write operation and throughput performance than write-back, but all data is written to non-volatile storage before confirmation to the host. However, write-through cache does not mirror the write data to the other controller cache because the data is written to the disk before posting command completion and cache mirroring is not required. You can set conditions that cause the controller to change from write-back caching to write-through caching. Please refer to the HP MSA 1040/2040 User Guide for ways to set the auto write through conditions correctly. In most situations, the default settings are acceptable.
In both caching strategies, active-active failover of the controllers is enabled.
Optimizing read-ahead caching
You can optimize a volume for sequential reads or streaming data by changing its read ahead, cache settings. Read ahead is triggered by sequential accesses to consecutive LBA ranges. Read ahead can be forward (that is, increasing LBAs) or reverse (that is, decreasing LBAs). Increasing the read-ahead cache size can greatly improve performance for multiple sequential read streams. However, increasing read-ahead size will likely decrease random read performance.
• Adaptive—this option works well for most applications: it enables adaptive read-ahead, which allows the controller to dynamically calculate the optimum read-ahead size for the current workload. This is the default.
• Stripe—this option sets the read-ahead size to one stripe. The controllers treat non-RAID and RAID 1 Disk Groups internally as if they have a stripe size of 512 KB, even though they are not striped.
• Specific size options—these options let you select an amount of data for all accesses.
• Disabled—this option turns off read-ahead cache. This is useful if the host is triggering read ahead for what are random accesses. This can happen if the host breaks up the random I/O into two smaller reads, triggering read ahead.
Caution
Only change read-ahead cache settings if you fully understand how the host operating system, application, and adapter move data so that you can adjust the settings accordingly.
Optimizing cache modes
You can also change the optimization mode for each volume.
• Standard—this mode works well for typical applications where accesses are a combination of sequential and random; this method is the default. For example, use this mode for transaction-based and database update applications that write small files in random order.
• No-mirror—in this mode each controller stops mirroring its cache metadata to the partner controller. This improves write I/O response time but at the risk of losing data during a failover. Unified LUN presentation (ULP) behavior is not affected, with the exception that during failover any write data in cache will be lost. In most conditions No-mirror is not recommended, and should only be used after careful consideration.
Parameter settings for performance optimization
You can configure your storage system to optimize performance for your specific application by setting the parameters as shown in table 2. This section provides a basic starting point for fine-tuning your system, which should be done during performance baseline modeling.
Table 2. Optimizing performance for your application
Application
RAID level
Read-ahead cache size
Cache write optimization
Default
5 or 6
Adaptive
Standard
High-Performance Computing (HPC)
5 or 6
Adaptive
Standard
Mail spooling
1
Adaptive
Standard
NFS_Mirror
1
Adaptive
Standard
Oracle_DSS
5 or 6
Adaptive
Standard
Oracle_OLTP
5 or 6
Adaptive
Standard
Oracle_OLTP_HA
10
Adaptive
Standard
Random 1
1
Stripe
Standard
Random 5
5 or 6
Stripe
Standard
Sequential
5 or 6
Adaptive
Standard
Sybase_DSS
5 or 6
Adaptive
Standard
Sybase_OLTP
5 or 6
Adaptive
Standard
Sybase_OLTP_HA
10
Adaptive
Standard
Video streaming
1 or 5 or 6
Adaptive
Standard
Exchange database
5 for data; 10 for logs
Adaptive
Standard
SAP®
10
Adaptive
Standard
SQL
5 for data; 10 for logs
Adaptive
Standard
Other methods to enhance array performance
There are other methods to enhance performance of the HP MSA 1040/2040. In addition to the cache settings, the performance of the HP MSA 1040/2040 array can be maximized by using the following techniques.
Place higher performance SSD and SAS drives in the array enclosure
The HP MSA 1040/2040 controller is designed to have a single SAS link per drive in the array enclosure and only four SAS links to expansion enclosures. Placing higher performance drives (i.e., SSD for HP MSA 2040 only and Enterprise SAS drives for both the HP MSA 1040 and HP MSA 2040) in the storage enclosure allows the controller to utilize the performance of those drives more effectively than if they were placed in expansion enclosures. This process will help generate better overall performance.
Fastest throughput optimization
The following guidelines list the general best practices to follow when configuring your storage system for fastest throughput:
• Host ports should be configured to match the highest speed your infrastructure supports.
• Disk Groups should be balanced between the two controllers.
• Disk drives should be balanced between the two controllers.
• Cache settings should be set to match table 2 (“Optimizing performance for your application”) for the application.
• In order to get the maximum sequential performance from a Disk Group, you should only create one volume per Disk Group. Otherwise you will introduce randomness into the workload when multiple volumes on the Disk Group are being exercised concurrently.
• Distribute the load across as many drives as possible.
• Distribute the load across multiple array controller host ports.
Creating Disk Groups
When creating Disk Groups, best practice is to add them evenly across both controllers when using linear storage or across both pools when using virtual storage. With at least one Disk Group assigned to each controller, both controllers are active. This active-active controller configuration allows maximum use of a dual-controller configuration’s resources.
Choosing the appropriate RAID levels
Choosing the correct RAID level when creating Disk Groups can be important for performance. However, there are some trade-offs with cost when using the higher fault tolerant RAID levels.
See table 3 below for the strengths and weaknesses of the supported HP MSA 1040/2040 RAID types.
Table 3. HP MSA 1040/2040 RAID levels
RAID level
Minimum disks
Allowable disks
Description
Strengths
Weaknesses
NRAID
1
1
Non-RAID, non-striped mapping to a single disk
Ability to use a single disk to store additional data
Not protected, lower performance (not striped)
0
2
16
Data striping without redundancy
Highest performance
No data protection: if one disk fails all data is lost
1
2
2
Disk mirroring
Very high performance and data protection; minimal penalty on write performance; protects against single disk failure
High redundancy cost overhead: because all data is duplicated, twice the storage capacity is required
3
3
16
Block-level data striping with dedicated parity disk
Excellent performance for large, sequential data requests (fast read); protects against single disk failure
Not well-suited for transaction-oriented network applications; write performance is lower on short writes (less than 1 stripe)
5
3
16
Block-level data striping with distributed parity
Best cost/performance for transaction-oriented networks; very high performance and data protection; supports multiple simultaneous reads and writes; can also be optimized for large, sequential requests; protects against single
Write performance is slower than RAID 0 or RAID 1
Table 3. HP MSA 1040/2040 RAID levels (continued)
RAID level
Minimum disks
Allowable disks
Description
Strengths
Weaknesses
6
4
16
Block-level data striping with double distributed parity
Best suited for large sequential workloads; non-sequential read and sequential read/write performance is comparable to RAID 5; protects against dual disk failure
Higher redundancy cost than RAID 5 because the parity overhead is twice that of RAID 5; not well-suited for transaction-oriented network applications; non-sequential write performance is slower than RAID 5
10
(1+0)
4
16
Stripes data across multiple RAID 1 sub-Disk Groups
Highest performance and data protection (protects against multiple disk failures)
High redundancy cost overhead: because all data is duplicated, twice the storage capacity is required; requires minimum of four disks
50
(5+0)
6
32
Stripes data across multiple RAID 5 sub-Disk Groups
Better random read and write performance and data protection than RAID 5; supports more disks than RAID 5; protects against multiple disk failures
Lower storage capacity than RAID 5
Note
RAID types NRAID, RAID 0, and RAID 3 can only be created using the Command Line Interface (CLI) and are not available in the SMU. When using Virtual Storage, only non-fault tolerant RAID types can be used in the Performance, Standard, and Archive and Tiers. NRAID and RAID 0 are used with Read Cache as the data in the Read Cache SSDs is duplicated on either the Standard or Archive Tier.
Volume mapping
For increased performance, access the volumes from the ports on the controller that owns the Disk Group, which would be the preferred path. Accessing the volume on the non-preferred path results in a slight performance degradation.
Optimum performance with MPIO can be achieved with volumes mapped to multiple paths on both controllers. When the appropriate MPIO drivers are installed on the host, only the preferred (optimized) paths will be used. The non-optimized paths will be reserved for failover.
Best practices for SSDs
SSDs are supported in the MSA 2040 system only. The performance capabilities of SSDs are a great alternative to traditional spinning hard disk drives (HDD) in highly random workloads. SSDs cost more in terms of dollars per GB throughput than spinning hard drives; however, SSDs cost much less in terms of dollars per IOP. Keep this in mind when choosing the numbers of SSDs per MSA 2040 array.
Use SSDs for randomly accessed data
The use of SSDs can greatly enhance the performance of the array. Since there are no moving parts in the drives, data that is random in nature can be accessed much faster.
Data such as database indexes and TempDB files would best be placed on a volume made from an SSD based Disk Group since this type of data is accessed randomly.
Another good example of a workload that would benefit from the use of SSDs is desktop virtualization, for example, virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) where boot storms require high performance with low latency.
SSD and performance
There are some performance characteristics which can be met with linear scaling of SSDs. There are also bandwidth limits in the MSA 2040 controllers. There is a point where these two curves intersect. At the intersecting point, additional SSDs will not increase performance. See figure 8.
The MSA 2040 reaches this bandwidth at a low number of SSDs. For the best performance using SSDs on the MSA 2040, use a minimum of 4 SSDs with 1 mirrored pair of drives (RAID 1) per controller. RAID 5 and RAID 6 are also good choices for SSDs, but require more drives using the best practice of having one Disk Group owned by each controller. This would require 6 SSDs for RAID 5 and 8 SSDs for RAID 6. All SSD volumes should be contained in fault tolerant Disk Groups for data integrity.
Base the number of SSDs to use on the amount of space that is needed for your highly random, high performance data set. For example, if the amount of data that is needed to reside in the SSD volumes exceeds a RAID 1 configuration, use a RAID 5 configuration.
Figure 11. SSD performance potential vs. MSA 2040 controller limit
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
Note
There is no limit to the number of SSDs that can be used in the MSA 2040 array system.
SSD Read Cache
SSD Read Cache is a feature that extends the MSA 2040 controller cache.
Read cache is most effective for workloads that are high in random reads. The user should size the read cache capacity based on the size of the hot data being randomly read. A maximum of 2 SSD drives per pool can be added for read cache.
HP recommends beginning with 1 SSD assigned per storage pool for read cache. Monitor the performance of the read cache and add more SSDs as needed.
Note
You can have SSDs in a fault tolerant Disk Group as a Performance Tier or as a non-fault tolerant (up to 2 disks) Disk Group as Read Cache. But neither pool can have both a Performance Tier and a Read Cache. For example, pool A can have a Performance Tier and pool B can have a Read Cache.
SSD wear gauge
SSDs have a limited number of times they can be written and erased due to the memory cells on the drives. The SSDs in the HP MSA 2040 come with a wear gauge as well as appropriate events that are generated to help detect the failure. Once the wear gauge reaches 0%, the integrity of the data is not guaranteed.
Best practice is to replace the SSD when the events and gauge indicate <5% life remaining to prevent data integrity issues.
Full Disk Encryption
Full Disk Encryption (FDE) is a data security feature used to protect data on disks that are removed from a storage array. The FDE feature uses special Self-Encrypting Drives (SED) to secure user data. FDE functionality is only available on the MSA 2040.
The SED is a drive with a circuit built into the drive’s controller chipset which encrypts/decrypts all data to and from the media automatically. The encryption is part of a hash code which is stored internally on the drive’s physical medium. In the event of a failure of the drive or the theft of a drive, a proper key sequence needs to be entered to gain access to the data stored within the drive.
Full Disk Encryption on the MSA 2040
The MSA 2040 storage system uses a passphrase to generate a lock key to enable securing the entire storage system. All drives in a Full Disk Encryption (FDE) secured system are required to be SED (FDE Capable). By default, a system and SED drive are not secured and all data on the disk may be read/written by any controller. The encryption on the SED drive conforms to FIPS 140-2.
To secure an MSA 2040, you must set a passphrase to generate a lock key and then FDE secure the system. Simply setting the passphrase does not secure the system. After an MSA 2040 system has been secured, all subsequently installed disks will automatically be secured using the system lock key. Non-FDE capable drives will be unusable in a secured MSA 2040 system.
Note
The system passphrase should be saved in a secure location. Loss of the passphrase could result in loss of all data on the MSA 2040 Storage System.
All MSA 2040 storage systems will generate the same lock key with the same passphrase. It is recommended that you use a different passphrase on each FDE secured system. If you are moving the entire storage system, it is recommended to clear the FDE keys prior to system shutdown. This will lock all data on the disks in case of loss during shipment. Only clear the keys after a backup is available and the passphrase is known. Once the system is in the new location, enter the passphrase and the SED drives will be unlocked with all data available.
SED drives which fail in an FDE secured system can be removed and replaced. Data on the drive is encrypted and cannot be read without the correct passphrase.
Best practices for Disk Group expansion
With the ever changing storage needs seen in the world today, there comes a time when storage space gets exhausted quickly. The HP MSA 1040/2040 gives you the option to grow the size of a LUN to keep up with your dynamic storage needs.
A Disk Group expansion allows you to grow the size of a Disk Group in order to expand an existing volume or create volumes from the newly available space on the Disk Group. Depending on several factors, Disk Group expansion can take a significant amount of time to complete. For faster alternatives, see the “Disk Group expansion recommendations” section.
Note
Disk Group Expansion is not supported with Virtual Storage. If you have Virtual Storage and are running out of storage space, the procedure to get more storage space would be to add another Disk Group to a pool.
The factors that should be considered with respect to Disk Group expansion include but are not limited to:
• Physical disk size
• Number of disks to expand (1–4)
• I/O activity during Disk Group expansion
Note
Disk Group Expansion is only available when using Linear Storage.
During Disk Group expansion, other disk utilities are disabled. These utilities include Disk Group Scrub and Rebuild.
Disk Group expansion capability for supported RAID levels
The chart below gives information on the expansion capability for the HP MSA 2040 supported RAID levels.
Expansion capability for each RAID level
RAID level
Expansion capability
Maximum disks
NRAID
Cannot expand
1
0, 3, 5, 6
Can add 1–4 disks at a time
16
1
Cannot expand
2
10
Can add 2 or 4 disks at a time
16
50
Can expand the Disk Group one RAID 5 sub-Disk Group at a time. The added RAID 5
sub-Disk Group must contain the same number of disks as each original sub-Disk Group
32
Important
If during the process of a Disk Group expansion one of the disk members of the Disk Group fails, the reconstruction of the Disk Group will not commence until the expansion is complete. During this time, data is at risk with the Disk Group in a DEGRADED or CRITICAL state.
If an expanding Disk Group becomes DEGRADED (e.g., RAID 6 with a single drive failure) the storage administrator should determine the level of risk of continuing to allow the expansion to complete versus the time required to backup, re-create the Disk Group (see “Disk Group expansion recommendations”) and restore the data to the volumes on the Disk Group.
If an expanding Disk Group becomes CRITICAL (e.g., RAID 5 with a single drive failure) the storage administrator should immediately employ a backup and recovery process. Continuing to allow the expansion places data at risk of another drive failure and total loss of all data on the Disk Group.
Disk Group expansion can be very time consuming. There is no way to reliably determine when the expansion will be complete and when other disk utilities will be available.
Follow the procedure below.
1. Backup the current data from the existing Disk Group.
2. Using the WBI or CLI, start the Disk Group expansion.
3. Monitor the Disk Group expansion percentage complete.
Note
Once a Disk Group expansion initiates it will continue until completion or until the Disk Group is deleted.
Disk Group expansion recommendations
Before expanding a Disk Group, review the information below to understand the best alternative method for allocating additional storage to hosts.
Allocate “quiet” period(s) to help optimize Disk Group expansion
Disk Group expansion can take a few hours with no data access for smaller capacity hard drives and may take several days to complete with larger capacity hard drives. Priority is given to host I/O or data access over the expansion process during normal array operation. While the system is responding to host I/O or data access requests, it may seem as if the expansion process has stopped. When expanding during “quiet” periods, expansion time is minimized and will allow quicker restoration of other disk utilities.
This method of expansion utilizes the expand capability of the system and requires manual intervention from the administrator. The procedure below outlines the steps to expand a Disk Group during a “quiet” period.
In this context, a “quiet” period indicates a length of time when there is no host I/O or data access to the system. Before starting the Disk Group expansion:
1. Stop I/O to existing volumes on the Disk Group that will be expanded.
2. Backup the current data from the existing volumes on the Disk Group.
3. Shutdown all hosts connected to the HP MSA 1040/2040 system.
4. Label and disconnect host side cables from the HP MSA 1040/2040 system.
Start and monitor Disk Group expansion:
1. Using the WBI or CLI, start the Disk Group expansion.
2. Monitor the Disk Group expansion percentage complete.
When expansion is complete or data access needs to be restored:
1. Re-connect host side cables to the HP MSA 1040/2040 system.
2. Restart hosts connected to the HP MSA 1040/2040 system.
If additional “quiet” periods are required to complete the Disk Group expansion:
1. Shutdown all hosts connected to the HP MSA 1040/2040 system.
2. Label and disconnect host side cables from the HP MSA 1040/2040 system.
3. Monitor the Disk Group expansion percentage complete.
Re-create the Disk Group with additional capacity and restore data
This method is the easiest and fastest method for adding additional capacity to a Disk Group. The online Disk Group initialization allows a user to access the Disk Group almost immediately and will complete quicker than the expansion process on a Disk Group that is also servicing data requests. The procedure below outlines the steps for recreating a Disk Group with additional capacity and restoring data to that Disk Group.
Procedure:
1. Stop I/O to existing volumes on the Disk Group that will be expanded.
2. Backup the current data from the existing volumes on the Disk Group.
3. Delete the current Disk Group.
4. Using the WBI or CLI, create a new Disk Group with the available hard drives using online initialization.
5. Create new larger volumes as required.
6. Restore data to the new volumes.
Best practices for firmware updates
The sections below detail common firmware update best practices for the MSA 1040/2040.
General MSA 1040/2040 device firmware update best practices
• As with any other firmware upgrade, it is a recommended best practice to ensure that you have a full backup prior to the upgrade.
• Before upgrading the firmware, make sure that the storage system configuration is stable and is not being reconfigured or changed in any way. If any configurations changes are in progress, monitor them using the SMU or CLI and wait until they are completed before proceeding with the upgrade.
• Do not power cycle or restart devices during a firmware update. If the update is interrupted or there is a power failure, the module could become inoperative. Should this happen, contact HP customer support.
• After the device firmware update process is completed, confirm the new firmware version is displayed correctly via one of the MSA management interfaces—e.g., SMU or CLI.
MSA 1040/2040 array controller or I/O module firmware update best practices
• The array controller (or I/O module) firmware can be updated in an online mode only in redundant controller systems.
• When planning for a firmware upgrade, schedule an appropriate time to perform an online upgrade.
– For single controller systems, I/O must be halted.
– For dual controller systems, because the online firmware upgrade is performed while host I/Os are being processed, I/O load can impact the upgrade process. Select a period of low I/O activity to ensure the upgrade completes as quickly as possible and avoid disruptions to hosts and applications due to timeouts.
• When planning for a firmware upgrade, allow sufficient time for the update.
– In single-controller systems, it takes approximately 10 minutes for the firmware to load and for the automatic controller restart to complete.
– In dual-controller systems, the second controller usually takes an additional 20 minutes, but may take as long as one hour.
• When reverting to a previous version of the firmware, ensure that the management controller (MC) Ethernet connection of each storage controller is available and accessible before starting the downgrade.
– When using a Smart Component firmware package, the Smart Component process will automatically first disable partner firmware update (PFU) and then perform downgrade on each of the controllers separately (one after the other) through the Ethernet ports.
– When using a binary firmware package, first disable the PFU option and then downgrade the firmware on each of the controller separately (one after the other).
MSA 1040/2040 disk drive firmware update best practices
• Disk drive upgrades on the HP MSA 1040/2040 storage systems is an offline process. All host and array I/O must be stopped prior to the upgrade.
• If the drive is in a Disk Group, verify that it is not being initialized, expanded, reconstructed, verified, or scrubbed. If any of these tasks is in progress, before performing the update wait for the task to complete or terminate it. Also verify that background scrub is disabled so that it doesn’t start. You can determine this using SMU or CLI interfaces. If using a firmware smart component, it would fail and report if any of the above pre-requisites are not being met.
• Disk drives of the same model in the storage system must have the same firmware revision. If using a firmware smart component, the installer would ensure all the drives are updated.
Miscellaneous best practices
Boot from storage considerations
When booting from SAN, the best option is to create a linear Disk Group and allocate the entire Disk Group as a single LUN for the host boot device. This can improve performance for the boot device and avoid I/O latency in a highly loaded array. Booting from LUNs provisioned from pools where the volumes share all the same physical disks as the data volumes is also supported, but is not the best practice.
8Gb/16Gb switches and small form-factor pluggable transceivers
The HP MSA 2040 storage system uses specific small form-factor pluggable (SFP) transceivers that will not operate in the HP 8Gb and 16Gb switches. Likewise, the HP Fibre Channel switches use SFPs which will not operate in the HP MSA 2040.
The HP MSA 2040 controllers do not include SFPs. Qualified SFPs for the HP MSA 2040 are available for separate purchase in 4 packs. Both 8G and 16G SFPs are available to meet the customer need and budget constraints. All SFPs in an HP MSA 2040 should conform to the installation guidelines given in the product Quick Specs. SFP speeds and protocols can be mixed, but only in the specified configurations.
In the unlikely event of an HP MSA 2040 controller or SFP failure, a field replacement unit (FRU) is available. SFPs will need to be moved from the failed controller to the replacement controller.
Please see the HP Transceiver Replacement Instructions document for details found at hp.com/support/msa2040/manuals.
The MSA 1040 8Gb Dual Controller FC arrays include 8Gb FC SFPs in all ports. These are the same 8Gb FC SFPs available for the MSA 2040 and will only function in MSA arrays.
In the unlikely event of an HP MSA 1040 controller or SFP failure, a field replacement unit (FRU) is available. SFPs will need to be moved from the failed controller to the replacement controller.
MSA 1040/2040 iSCSI considerations
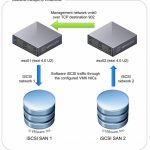
When using the MSA 2040 SAN controller in an iSCSI configuration or using the MSA 1040 1GbE or 10GbE iSCSI storage systems, it is a best practice to use at least three network ports per server, two for the storage (Private) LAN and one or more for the Public LAN(s).This will ensure that the storage network is isolated from the other networks.
The Private LAN is the network that goes from the server to the MSA 1040 iSCSI or MSA 2040 SAN controller. This Private LAN is the storage network and the Public LAN is used for management of the MSA 1040/2040. The storage network should be isolated from the Public LAN to improve performance.
Figure 12. MSA 2040 SAN iSCSI Network
استوریج-های-HP-MSA-2040-1040-قیمت-مشاوره-فنی
IP address scheme for the controller pair
The MSA 2040 SAN controller in iSCSI configurations or the MSA 1040 iSCSI should have ports on each controller in the same subnets to enable preferred path failover. The suggested means of doing this is to vertically combine ports into subnets. See examples below.
Example with a netmask of 255.255.255.0:
MSA 2040 SAN:
Controller A port 1: 10.10.10.100
Controller A port 2: 10.11.10.110
Controller A port 3: 10.10.10.120
Controller A port 4: 10.11.10.130
Controller B port 1: 10.10.10.140
Controller B port 2: 10.11.10.150
Controller B port 3: 10.10.10.160
Controller B port 4: 10.11.10.170
MSA 1040 iSCSI:
Controller A port 1: 10.10.10.100
Controller A port 2: 10.11.10.110
Controller B port 1: 10.10.10.120
Controller B port 2: 10.11.10.130
Jumbo frames
A normal Ethernet frame can contain 1500 bytes whereas a jumbo frame can contain a maximum of 9000 bytes for larger data transfers. The MSA reserves some of this frame size; the current maximum frame size is 1400 for a normal frame and 8900 for a jumbo frame. This frame maximum can change without notification. If you are using jumbo frames, make sure to enable jumbo frames on all network components in the data path.
Summary
HP MSA 1040/2040 administrators should determine the appropriate levels of fault tolerance and performance that best suits their needs. Understanding the workloads and environment for the MSA SAN is also important. Following the configuration options listed in this paper can help optimize the HP MSA 1040/2040 array accordingly.
POWERED BY
Create Your Own Free Website
A surprisingly easy drag & drop site creator.Learn more.